



1. Polarized Capacitor
These capacitors are suitable for DC circuits. Identify correctly the polarity of the capacitor before use. Incorrect application of polarity may cause short
circuit or venting.
2. Bi-Polar Capacitors
Bi-polar type of capacitor is for a circuit where the polarity is occasionally
reversed. However, take note that a bi-polar capacitor should not be used for
AC voltage application.
3. Operating Voltage
Do not apply a DC voltage which exceeds the rated voltage. The peak voltage
of a superimposed (ripple current) on the DC capacitor must not exceed the
rated voltage.
A surge voltage value which exceeds the full rated voltage is prescribed in the
catalog, but the application should be restricted to short period of time.
4. Ripple Current
Ripple current exceeding the permissible value will cause heat on the capacitor,
and may decrease the capacitance or damage the capacitor.
Ripple current on the capacitor must be at or below allowable level. Generally,
not more than 80% of the rated current. There is a specified rated ripple current
correspond to the ripple frequency. The rated ripple current at a certain
frequency must be calculated by multiplying the rated ripple current by a factor.
5. Operating Temperature Range
The characteristics of capacitors change with the operating temperature. The
capacitance and leakage current increase and dissipation factor decreases at
higher temperature. The use of a capacitor exceeding the maximum rated
temperature will considerably shorten the life or cause the capacitor to vent.
Usage at lower temperature can ensure longer lifetime. The lifetime is
approximately halved with each 10°C rise in ambient temperature.
6. Operating Frequency
The capacitance of the electrolytic capacitors is usually measured at 120Hz.
However, the capacitance will decrease and dissipation factor increases as the
applied frequency becomes higher. If a capacitor is to be used at higher
frequency, you may need a specially designed capacitor that is suitable for the
purpose. Please contact our technical team.
7. Charge and Discharge
Do not use the general purpose capacitors in circuits where frequent heavy
charge and discharge cycles are required. Frequent, sharp, heavy, charge and
discharge cycles will result in decrease in capacitance and damage to the
capacitor due to the excessive generated heat. Specific capacitors can be
designed to meet the requirements of charging and discharging cycles. Please
tell us your requirement.
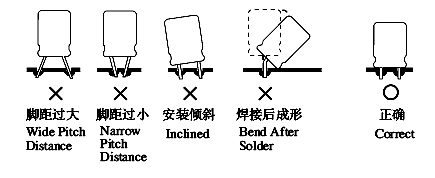
8. Installing Capacitors
The excessive external force applied to terminals or lead wires may cause high
leakage current, short /open circuit or leakage of electrolytic liquid. Make sure
that the leads spacing of the capacitor matches the hole spacing of the PC board
prior to installation.
If the terminals spacing of a capacitor does not fit the hole spacing of the PC
board, adjust the terminals carefully so as not to cause mechanical stress to the
capacitors. The following are typical examples of stress to capacitors that should
be avoided:
9. Soldering Temperature
9.1 Flow soldering (wave solder)
To avoid crack sleeve and damage to capacitor, the recommended solder temperature should be within <260ºC and at a duration of <10 seconds. Avoid having flux on any surfaces except on the terminals and contact point between the board and the aluminum capacitor.
9.2 Hand soldering
Recommended solder temperature is at <350ºC and the duration at <4 seconds.
10. Cleaning after Soldering
To prevent damage to sleeve, markings and sealing materials, the capacitor
should never be washed with halogenous solvents such as trichlorethylene,
xylene or acetone and the like. Recommended cleaning solvents are methanol,
isopropanol, ethanol, isobutanol, petroleumether, propanol and commercial
detergents.
11. Storage and Voltage Treatment
During long storage, DC leakage current of aluminum electrolytic capacitors will
increase. In order to prevent heat rise and high DC leakage current, voltage
treatment is recommended especially for capacitor which have been stored for
more than 2 years at room temperature.
The capacitors shall be applied with DC voltage, increasing it gradually to the
rated voltage at room temperature. The voltage shall be maintained until DC
leakage current comes down to the specified value or less.
12. Safety Vent
When ventinh, a capacitor gives out gas with a temperature of over 100ºC.
Protect your face and eyes when working on the capacitors.
In the case of a short-circuit, the aluminum electrolytic capacitor will vent and
expel gas. It is suggested to provide sufficient space between the vent of
capacitor with the cover or adjacent components. There should not be any
conductive material placed above the safety vent. The following spacing is
recommended:
![]()


